1.Python多线程机制
a.GIL与线程调度
b.初见Python Thread
c.Python线程的创建
[threadmodule.c]
static PyObject* thread_PyThread_start_new_thread(PyObject* self, PyObject* fargs){
PyObject* func, *args, *keyw = NULL;
struct bootstate* boot;
long ident;
PyArg_UnpackTuple(fargs,"start_new_thread",2,3,&func,&args,&keyw);
//创建bootstate结构
boot = PyMem_NEW(struct bootstate, 1);
boot->interp = PyThreadState_GET()->interp;
boo->func = func;
boot->args = args;
boot->keyw - keyw;
//初始化多线程环境.当Python启动时,是不支持多线程的
PyEval_InitThreads(); /* Start the interpreter's thread-awareness */
//创建线程
ident = PyThread_start_new_thread(t_bootstrap,(void *)boot);
return PyInt_FromLong(ident);
}
建立多线程环境
[pythread.h]
typedef void* PyThread_type_lock;
[ceval.c]
static PyThread_type_lock interpreter_lock = 0; // GIL
static long main_thread = 0;
void PyEval_InitThreads(void){
if(interpreter_lock)
return;
interpreter_lock = PyThread_allocate_lock();
PyThread_acquire_lock(interpreter_lock,1);
main_thread = PyThread_get_thread_ident();
}
[thread_nt.h]
PyThread_type_lock PyThread_allocate_lock(void){
PNRMUTEX aLock;
if(!initialized)
PyThread_init_thread();
aLock = AllocNonRecursiveMutex();
return (PyThread_type_lock) aLock;
[thead.c]
void PyThread_init_thread(void){
if(initialized)
return;
initialized = 1;
PyThread__init_thread();
}
[thread_nt.h]
static void PyThread__init_thread(void) {}
}
[thread_nt.h]
typedef struct NRMUTEX{
LONG owned;
DWORD thread_id;
HANDLE hevent;
} NRMUTEX, *PNRMUTEX
[thread_nt.h]
PNRMUTEX AllocNonRecursiveMutex(void){
PNRMUTEX mutex = (PNRMUTEX)malloc(sizeof(NRMUTEX));
if(mutex && !InitializeNonRecursiveMutex(mutex)){
free(mutex);
Mutex = NULL;
}
return mutex;
}
BOOL InitializeNonRecursiveMutex(PNRMUTEX mutex){
...
mutex->owned = -1; /* No threads have entered NonRecursiveMutex */
mutex->thread_id = 0;
mutex->hevent = CreadEvent(NULL,FALSE,FALSE,NULL);
return mutex->hevent != NULL; /* True if the mutex is created */
}
//获得GIL
[thread_nt.h]
int PyThread_acquire_lock(PyThread_type_lock aLock, int waitflag){ //waitflag指示当GIL当前不可获得时,是否进行等待
int success;
success = aLock && EnterNonRecursiveMutex((PNRMUTEX) aLock, (waitflag == 1 ? INFINITE : 0)) == WAIT_OBJECT_0;
return success;
}
DWORD EnterNonRecursiveMutex(PNRMUTEX mutex, BOOL wait){
/* Assume that the thread waits successfully */
DWORD ret;
/* InterlockedIncrement(&mutex->owned) == 0 means no thread currently owns the mutex */
if(!wait){
if(InterlockedCompareExchange((PVOID *)&mutex->owned,(PVOID)0,(PVOID) -1) != (PVOID) - 1)
return WAIT_TIMEOUT;
ret = WAIT_OBJECT_0;
}else{
ret = InterlockedIncrement(&mutex->owned) ? WaitForSingleObject(mutex->hevent,INFINITE) : WAIT_OBJECT_0;
}
mutex->thread_id = GetCurrentThreadId(); /* we own it */
return ret;
}
//PyThread_acquire_lock的逆运算PyThread_release_lock
[thread_nt.h]
void PyThread_release_lock(PyThread_type_lock aLock){
LeaveNonRecursiveMutex((PNRMUTEX)aLock);
}
BOOL LeaveNonRecursiveMutex(PNRMUTEX mutex){
/* We don't own the mutex */
mutex->thread_id = 0;
return InterlockedDecrement(&mutex->owned) < 0 || SetEvent(mutex->hevent); /* Other threads are waiting, wake one on them up */
}

创建线程
子线程的诞生
[threadmodule.c]
static PyObject* thread_PyThread_start_new_thread(PyObject* self, PyObject* fargs){
PyObject* func, *args, *keyw = NULL;
struct bootstate* boot;
long ident;
PyArg_UnpackTuple(fargs,"start_new_thread",2,3,&func,&args,&keyw);
//创建bootstate结构
boot = PyMem_NEW(struct bootstate, 1);
boot->interp = PyThreadState_GET()->interp;
boo->func = func;
boot->args = args;
boot->keyw - keyw;
//初始化多线程环境.当Python启动时,是不支持多线程的
PyEval_InitThreads(); /* Start the interpreter's thread-awareness */
//创建线程
ident = PyThread_start_new_thread(t_bootstrap,(void *)boot);
return PyInt_FromLong(ident);
}
[thread.c]
/* Support for runtime thread stack size tuning.
A value of 0 means using the platform's default stack size
or the size specified by the THREAD_STACK_SIZE macro.
*/
static size_t _pythread_stacksize = 0;
[thread_nt.h]
long PyThread_start_new_thread(void (*func)(void *), void* arg){
unsigned long rv;
callobj obj;
obj.id = -1; /* guilty until proved innocent */
obj.func = func;
obj.arg = arg;
obj.done = CreateSemaphore(NULL,0,1,NULL);
rv = _beginthread(bootstrap,_pythread_stacksize,&obj); /* use default stack size */
if(rv == (unsigned long) - 1){
//创建raw thread 失败
obj.id = -1;
}else{
WaitForSingleObject(obj.done,INFINITE);
}
CloseHandle((HANDLE)obj.done);
return obj.id;
}
[thread_nt.h]
typedef struct {
void (*func)(void *);
void *arg;
long id;
HANDLE done;
} callobj;

[thread_nt.h]
static int bootstrap(void *call){
callobj* obj = (callobj *)call;
/* copy callobj since other thread might free it before we're done */
//这里将得到函数t_bootstrap
void (*func)(void*) = obj->func;
void *arg = obj->arg;
obj->id = PyThread_get_thread_ident();
ReleaseSemaphore(obj->done,1,NULL);
func(arg);
return 0;
}

[threadmodule.c]
static void t_bootstrap(void* boot_raw){
struct bootstate* boot = (struct bootstate *)boot_raw;
PyThreadState* tstate;
PyObject* res;
tstate = PyThreadState_New(boot->interp);
PyEval_AcquireThread(tstate);
res = PyEval_CallObjectWithKeywords(boot->func,boot->args,boot->keyw);
PyMem_DEL(boot_raw);
PyThreadState_Clear(tstate);
PyThreadState_DeleteCurrent();
PyThread_exit_thread();
}
[ceval.c]
void PyEval_AcquireThread(PyThreadState* tstate){
if(tstate == NULL)
Py_FatalError("PyEval_AcquireThread: NULL new thread state");
//检查interpreter_lock,确保已经调用PyEval_InitThreads并创建了GIL
assert(interpreter_lock);
//获得GIL
PyThread_acquire_lock(interpreter_lock,1);
//在PyThreadState_Swap中更新指向“当前线程”的线程状态对象指针_PyThreadState_Current
if(PyThreadState_Swap(tstate) != NULL)
Py_FatalError("PyEval_AcquireThread: non-NULL old thread state");
}
[pystate.c]
PyThreadState* PyThreadState_Swap(PyThreadState* newts){
PyThreadState* oldts = _PyThreadState_Current;
_PyThreadState_Current = newts;
return oldts;
}
线程状态保护机制
[pystate.h]
typedef struct _ts{
struct _ts *next;
PyInterpreterState* interp;
struct _frame* frame;
int recursion_depth;
...
int gilstate_counter;
long thread_id;
} PyThreadState;
[thread.c]
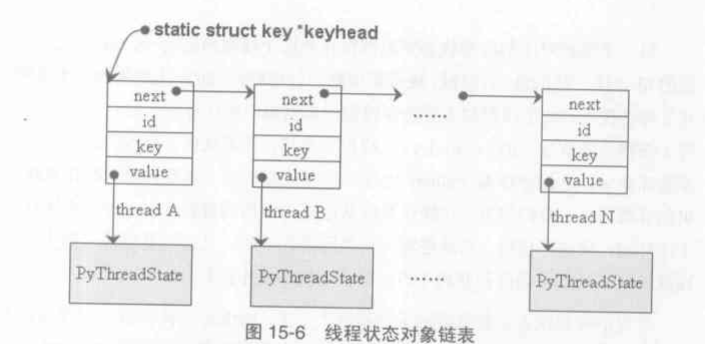
struct key{
struct key* next;
long id;
int key;
void* value;
};
static struct key* keyhead = NULL;
[pystate.c]
static PyInterpreterState* autoInterpreterState = NULL;
static int autoTLSkey = 0;
void _PyGILState_Init(PyInterpreterState* i,PyThreadState* t){
autoTLSkey = PyThread_create_key(); //TLS:Thread Local Store
autoInterpreterState = i;
/* Now stash the thread state for this thread in TLS */
assert(PyThread_get_key_value(autoTLSkey) == NULL);
_PyGILState_NoteThreadState(t);
...
}
static void _PyGILState_NoteThreadState(PyThreadState* tstate){
if(!autoTLSkey)
return;
PyThread_set_key_value(autoTLSkey,(void *)tstate);
tstate->gilstate_counter = 1;
}
[thread.c]
static PyThreadState_create_key(void){
if(keymutex == NULL)
keymutex = PyThread_allocate_lock(); //keymutex用来互斥对状态对象链表的访问
return ++nkeys;
}
[thread.c]
static struct key* find_key(int key,void* value){
struct key* p;
//获得当前线程的线程id,并锁住线程状态对象链表
long id = PyThread_get_thread_ident();
PyThread_acquire_lock(keymutex,1);
//遍历线程状态对象链表,寻找key和id都匹配的元素
for(p = keyhead; p != NULL; p = p->next){
if(p->id ==id && p->key == key)
goto Done;
}
//如果搜索失败,则创建新的元素,并加入线程状态对象链表
p = (struct key *)malloc(sizeof(struct key));
if(p != NULL){
p->id = id;
p->key = key;
p->next = keyhead;
keyhead = p;
}
Done:
//释放锁住的状态对象链表
PyThread_release_lock(keymutex);
return p;
}
[thread.c]
//查询操作
void* PyThread_get_key_value(int key){
struct key* p = find_key(key,NULL);
return p->value;
}
//插入操作
int PyThread_set_key_value(int key, void* value){
struct key* p = find_key(key,value);
return 0;
}
//删除操作
void PyThread_delete_key(int key){
struct key*p ,**q;
PyThread_acquire_lock(keymutex,1);
q = &keyhead;
while((p = *q) != NULL){
if(p->key == key){
*q = p->next;
free((void *)p);
}else{
q = &p->next;
}
PyThread_release_lock(keymutex);
}
}
从GIL到字节码解释器
[pystate.c]
PyThreadState* PyThreadState_New(PyInterpreterState* interp){
PyThreadState* tstate = (PyThreadState *)malloc(sizezof(PyThreadState));
...
#ifdef WITH_THREAD
_PyGILState_NoteThreadState(tstate);
#endif
...
return tstate;
}
当前活动的python线程不一定是获得了GIL的线程
当所有的线程都完成了初始化动作之后,操作系统的线程调度和Python的线程调度才会统一
进入Python解释器后才完成线程初始化(PyEval_EvalFrame)
d.Python线程的调度
标准调度
//加入线程调度机制的PyEval_EvalFrameEx
[ceval.c]
/* Interpreter main loop */
PyObject* PyEval_EvalFrameEx(PyFrameObject* f){
...
why = WHY_NOT;
for(;;){
...
if(--_Py_Ticker < 0){
//在切换线程之前,重置_Py_Ticker为100,为下一个线程准备
_Py_Ticker = _Py_CheckInterval;
tstate->tick_counter++;
if(interpreter_lock){
//撤销当前线程状态对象,释放GIL,给别的线程一个机会
PyThreadState_Swap(NULL);
PyThread_release_lock(interpreter_lock);
/*
由于等待GIL而被挂起的子线程被操作系统的线程调度机制唤醒,从而
进入PyEval_EvalFrameEx
对于主线程,虽然这时它已经失去了GIL,由于没有被挂起,所以对于
操作系统的线程调度机制,它是可以被再次切换为活动线程的
当操作系统的调度机制将主线程切换为活动线程之后,主线程将执行PyThread_acquire_lock,主线程申请GIL,由于被子线程占有,
主线程将自身挂起。
从这时起,操作系统的线程调度不能再将主线程切换为活动进行,直到子线程释放GIL
*/
//别的线程现在已经开始执行了,咱们重新在申请GIL,等待下一次被调度
PyThread_acquire_lock(interpreter_lock,1);
PyThreadState_Swap(tstate) != NULL;
}
}
...
}
}
[ceval.c]
int _Py_CheckInterval = 100;
volatile int _Py_Ticker = 100;
e.Python子线程的销毁
[threadmodule.c]
static void t_bootstrap(void* boot_raw){
struct bootstate* boot = (struct bootstate *)boot_raw;
PyThreadState* tstate;
PyObject* res;
tstate = PyThreadState_New(boot->interp);
PyEval_AcquireThread(tstate);
res = PyEval_CallObjectWithKeywords(boot->func,boot->args,boot->keyw);
PyMem_DEL(boot_raw);
PyThreadState_Clear(tstate);
PyThreadState_DeleteCurrent();
PyThread_exit_thread();
}
Python首先通过PyThreadState_Clear清理当前线程所对应的线程状态对象
//PyThreadState_DeleteCurrent释放GIL
[pystate.c]
void PyThreadState_DeleteCurrent(){
PyThreadState* tstate = _PyThreadState_Current;
_PyThreadState_Current = NULL;
tstate_delete_common(tstate);
if(autoTLSkey && PyThread_get_key_value(autoTLSkey) == tstate)
PyThread_delete_key_value(autoTLSkey);
PyEval_ReleaseLock();
}
Python最后通过PyThread_exit_thread完成各个平台上不同的销毁原声线程的工作
f.Python线程的用户级互斥与同步
用户级互斥与同步
Lock对象
[threadmodule.c]
static PyObject* thread_PyThread_allocate_lock(PyObject* self){
return (PyObject *)newlockobject();
}
static lockobject* newlockobject(void){
lockobject* self;
self = PyObject_New(lockobject,&Locktype);
self->lock_lock = PyThread_allocate_lock();
return self;
}
[pythread.h]
typedef void* PyThread_type_lock;
[threadmodule.c]
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
PyThread_type_lock lock_lock;
} lockobject;
[threadmodule.c]
static PyMethodDef lock_method[] = {
{"acquire_lock",(PyCFunction)lock_PyThread_acquire_lock,...}
{"acquire",(PyCFunction)lock_PyThread_acquire_lock,...}
{"release_lock",(PyCFunction)lock_PyThread_release_lock,...}
{"release",(PyCFunction)lock_PyThread_release_lock,...}
{"locked_lock",(PyCFunction)lock_locked_lock,...}
{"locked",(PyCFunction)lock_locked_lock,..}
{NULL,NULL} /* sentinel */
}
//申请用户级的lock,这个申请在lock.acquire中完成,对应的C函数为lock_PyThread_acquire_lock
[threadmodule.c]
static PyObject* lock_PyThread_acquire_lock(lockobject* self,PyObject* args){
//i中保存用户传入的参数,表示是否在lock资源不可用时将自身挂起,进行等待
int i = 1;
PyArg_ParseTuple(args,"|i:acquire",&i);
Py_BEGIN_ALLOW_THREADS
i = PyThread_acquire_lock(self->lock_lock,i)
Py_END_ALLOW_THREADS
}
static PyObject* lock_PyThread_release_lock(lockobject* self){
/* Sanity check: the lock must be locked */
if(PyThread_acquire_lock(self->lock_lock,0)){
PyThread_release_lock(self->lock_lock);
PyErr_SetString(ThreadError,"release unlocked lock");
return NULL;
}
PyThread_release_lock(self->lock_lock);
Py_INCREF(Py_None);
return Py_None;
}
g.高级线程库--threading
Threading Module 概述
[threading.py]
import thread
_start_new_thread = thread.start_new_thread
_allocate_lock = thread.allocate_lock
_get_ident = thread.get_ident
ThreadError = thread.error
[threading.py]
# Active thread administration
_active_limbo_lock = _allocate_lock()
_active = {} // _active[thread_id] = thread 已经创建子线程
_limbo = {} //_limbo[thread] = thread 在未创建原生子线程
# 列举当前所有子线程的操作
[threading.py]
def enumerate():
_active_limbo_lock.acquire()
active = _active.values() + _limbo.values()
_active_limbo_lock.release()
return active
Threading 的线程同步工具
[threading.py]
_allocate_lock = thread.allocate_lock
Lock = _allocate_lock
RLock
可重入的Lock
Condition
需要一个Lock对象作为参数,否则将在内部自行创建一个RLock对象,提供了wait和notify语义
Semaphore
Semaphore对象内部维护着一个Condition对象,管理共享资源池
Event
Threading 中的 Thread
[threading.py]
class Thread(_Verbose):
__initialized = False
def __init__(self,group=None, target=None, name=None, args=(),kwargs={},verbose=None):
...
self.__name = str(name or _newname())
self.__started = False
self.__stopped = False
self.__block = Condition(Lock())
self.__initialized = True
def start(self):
_active_limbo_lock.acquire()
_limbo[self] = self
_active_limbo_lock.release()
_start_new_thread(self.__bootstrap,{})
_sleep(0.000001)
def run(self):
if self.__target:
self.__target(*self.__args,**self.__kwargs)
def __bootstrap(self):
try:
self.__started = True
_active_limbo_lock.acquire()
_active[_get_ident()] = self
del _limbo[self]
_active_limbo_lock.release()
try:
self.run()
finally:
self.__stop()
try:
self.__delete()
except:
pass
def __stop(self):
self.__block.acquire()
self.__stopped = True
self.__block.notifyAll()
self.__block.release()
def join(self,timeout=None):
self.__block.acquire()
if timeout is None:
while not self.__stopped:
self.__block.wait()
else:
deadline = _time() + timeout
while not self.__stopped:
delay = deadline - _time()
if delay <= 0:
if __debug__:
self._note("%s.join(): timed out",self)
break
self.__block,wait(delay)
else:
if __debug__:
self._note("%s.joi(): thread stopped",self)
self.__block.release()